回溯类型的题目,大部分的模板都是三步骤:
- 判断终止条件,存储枚举结果
- 以某种方式遍历数组/集合,可以用visited数组辅助判断是否遍历过
- 进入下一层递归
- 恢复现场
全排列
有点不好理解,主要是dfs思想,固定第u位,然后for(int i = 0; i<length; i++);dfs(u+1)枚举
class Solution {
int length;
List<Integer> path; // 当前路径
List<List<Integer>> res; // 所有结果
int[] used; // 标记数组
int[] nums; // 原始数组
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
this.length = nums.length;
this.used = new int[length];
this.res = new ArrayList<>();
this.path = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int u) {
if (u == length) { // 终止条件:已选完所有数字
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 添加当前排列到结果集
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (used[i] == 0) { // 如果i号数字未被使用
used[i] = 1; // 标记为已使用
path.add(nums[i]); // 添加到当前路径
dfs(u + 1); // 递归下一层
path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯:移除最后添加的数字
used[i] = 0; // 回溯:标记为未使用
}
}
}
}
子集
二进制枚举,有或无的情况,用二进制枚举比较直观。用0表示不选用这一位的数,用非0表示选用。注意(i & ( 1 << j)) != 0条件应该是非0,而不是等于1,因为位运算的结果可能非1,例如i=010(2),1<<j=010,相与运算的结果非1。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int n = nums.length;
int cnt = (1 << n);
for(int i = 0; i < cnt; i++){
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if((i & ( 1 << j)) != 0){
// 说明当前枚举数字的第j位为1 加入
tmp.add(nums[j]);
}
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}
电话号码的字母组合
枚举,思路:dfs(u),u为输入数字串的位数,对数字串的每一位,用map取出可能的字符集,for循环这些字符集,在for中继续dfs(u+1)。
class Solution {
private List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
private StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
private Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<>();
private String digits;
private int length;
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return res;
}
this.digits = digits;
this.length = digits.length();
map.put('2', "abc");
map.put('3', "def");
map.put('4', "ghi");
map.put('5', "jkl");
map.put('6', "mno");
map.put('7', "pqrs");
map.put('8', "tuv");
map.put('9', "wxyz");
dfs(0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int u) {
if (u == length) {
res.add(tmp.toString());
return;
}
char digit = digits.charAt(u);
String letters = map.get(digit);
for (int i = 0; i < letters.length(); i++) {
tmp.append(letters.charAt(i));
dfs(u + 1);
tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
}
组合总数
定义递归函数 dfs(target,combine,idx)表示当前在 candidates 数组的第 idx 位,还剩 target 要组合,已经组合的列表为 combine。递归的终止条件为target≤0或者 candidates 数组被全部用完。那么在当前的函数中,每次我们可以选择:
- 跳过不用第 idx 个数,即执行 dfs(target,combine,idx+1)。
- 也可以选择使用第 idx 个数,即执行 dfs(target−candidates[idx],combine,idx),注意到每个数字可以被无限制重复选取,因此搜索的下标仍为 idx。
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> combine = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates, target, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int index){
if(index == candidates.length){
return;
}
if(target == 0){
res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combine));
return;
}
// 情况1 直接跳过
dfs(candidates, target, index + 1);
// 情况2 考虑
if(target -candidates[index] >= 0){
combine.add(candidates[index]);
// 当前index可以重复 不需要index + 1
dfs(candidates, target - candidates[index], index);
combine.remove(combine.size() - 1);
}
}
}
括号匹配
找到规律,即对于输入N,潜在的含义是,左右括号的数目不超过n,因此可以递归dfs(str, left, right),递归构造括号字符串,
- 当
left == right的时候,说明下一个括号只能是左括号 - 否则下一个括号可以左也可以右
- 递归终止条件为
left == 0 && right == 0括号都匹配完了
class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
if(n <= 0) return res;
dfs("", n, n);
return res;
}
// 参数分别为:当前构造的字符串, 能使用的左括号数目, 能使用的右括号数
public void dfs(String str, int left, int right){
if(left == 0 && right == 0){
res.add(str);
return;
}
if(left == right){
// 如果能使用的左右括号数相等 下一个只能用左括号
dfs(str + "(", left - 1, right);
}else if(left < right){
// 可以使用左括号 也可也使用右括号
if(left > 0) dfs(str + "(", left - 1, right);
if(right > 0) dfs(str + ")", left, right - 1);
}
return;
}
}
单词搜索
二维的递归,用visited[i][j]维护是否遍历到的情况。
class Solution {
boolean[][] visited;
int[][] dir = {{0,1}, {0,-1}, {1,0}, {-1,0}};
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
int row = board.length;
int col = board[0].length;
visited = new boolean[row][col];
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++){
if(dfs(board, i, j, word, 0)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j, String word, int index){
if(index == word.length()) return true;
// 在递归开始就判断条件 如果board[i][j] != word.charAt(index) 则终止递归 返回false
if(i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.length || j >= board[0].length ||
visited[i][j] || board[i][j] != word.charAt(index)){
return false;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
for(int[] d : dir){
int dx = i + d[0];
int dy = j + d[1];
if(dfs(board, dx, dy, word, index + 1)){
return true;
}
}
visited[i][j] = false;
return false;
}
}
分割回文串
- 我们从字符串的起始位置开始,尝试所有可能的分割点
- 对于每个可能的分割点,检查当前子串是否是回文
- 如果是回文,则继续递归处理剩余的字符串
class Solution {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> current = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrack(s, 0);
return result;
}
private void backtrack(String s, int index) {
// 到头了 无需再分 添加current进入答案中
if (index == s.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(current));
return;
}
for (int end = index + 1; end <= s.length(); end++) {
// 分割子串
String substring = s.substring(index, end);
if (isPalindrome(substring)) {
// 如果是回文串 就添加进current中 递归执行从end开始的分割回文串
current.add(substring);
backtrack(s, end);
current.remove(current.size() - 1); // 回溯
}
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
while (left < right) {
if (s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
N皇后
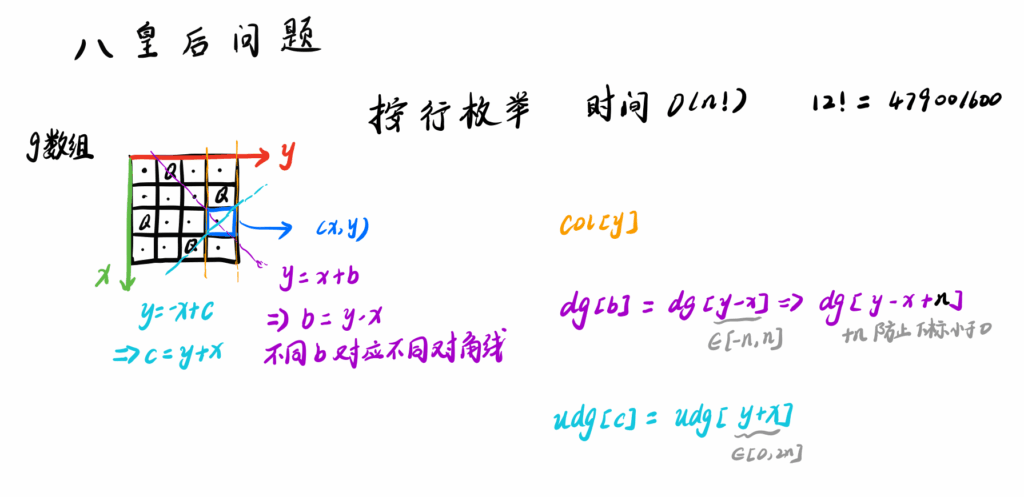
DFS枚举行数,每行必定有一个皇后。每层枚举的时候,判断斜线、反斜线、当前列有无皇后占用。 关键是如何维护visited数组,判断某个点的两个斜向有无皇后? 贴一个acwing的解答:AcWing 843. n-皇后问题(按行枚举或按每个元素枚举) – AcWing
对于某个点的斜线,其实可以用它的一元方程系数来唯一确定
- 比如,对于正斜线,
y = x + b,b可以用来定位整个棋盘的正斜线,因此,可以用b = y - x,来确定斜线visited数组,要注意y - x会小于0,因此要在前面加个系数保证它大于0即可。 - 同样,对于反斜线,可以用
y = -x + b,即b = x + y来定位。
class Solution {
List<String> cur = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// 当前列、正向、反向visited
boolean[] zx;
boolean[] fx;
boolean[] col;
int N;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
N = n;
zx = new boolean[2 * N];
fx = new boolean[2 * N];
col = new boolean[N];
dfs(0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int u){
if(u == N){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(cur));
}
int x = u;
for(int y = 0; y < N; y++){
// 正斜线系数b=y-x 需要加上N防止小于0
if(col[y] == false && zx[y - x + N] == false && fx[y + x] == false){
// 说明当前x y 是一个当前层的解
col[y] = true;
zx[y - x + N] = true;
fx[y + x] = true;
// 构造一个解
String tmp = handle(y);
cur.add(tmp);
dfs(u + 1);
// 出递归, 恢复现场
col[y] = false;
zx[y - x + N] = false;
fx[y + x] = false;
cur.remove(cur.size() - 1);
}
}
}
public String handle(int y){
// 第y位上有Q 其他位置上都是.
String res = "";
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
if(i == y) res += "Q";
else res += ".";
}
return res;
}
}