相交链表
找两个链表的相同节点,思想:求出两个链表长度,再让长的先走到和短的长度一样,之后一起走。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(headA != null){
len1++;
headA = headA.next;
}
while(headB != null){
len2++;
headB = headB.next;
}
if(len1 < len2){
int gap = len2 - len1;
while(gap != 0){
gap--;
curB = curB.next;
}
}else{
int gap = len1 - len2;
while(gap != 0){
gap--;
curA = curA.next;
}
}
while(curA != null && curB != null){
if(curA == curB) return curA;
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
反转链表
三指针迭代,pre、cur、next,pre作为一个dummy节点。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
回文链表
如果允许空间复杂度为O(n),可以将其值复制到数组或栈中进行处理,很直观。
没有用额外空间的方法,是将链表后半段反转,就可以用快慢指针一一对比出来。
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// slow 的位置就是要反转的位置
ListNode pre = null;
while(slow != null){
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = pre;
pre = slow;
slow = next;
}
// 不需要特判奇偶
ListNode cur = head;
while(pre != null){
if(pre.val != cur.val) return false;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return true;
}
}
环形链表
快慢指针。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 如果有环 快慢指针必定相遇
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(slow == fast) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
环形链表2
快慢指针相遇的地方,不一定就是入口节点。 用数学方式计算,可以得到结论:slow和head同时移动,相遇点是入口。
如下图,慢指针走了 a + b 的距离,快指针此时走了 a + b + n(b + c) 距离,并且快指针的速度是2倍的慢指针,所以能够得出 a = c+(n−1)(b+c) , 即让slow和head同时移动,相遇点就是入口。
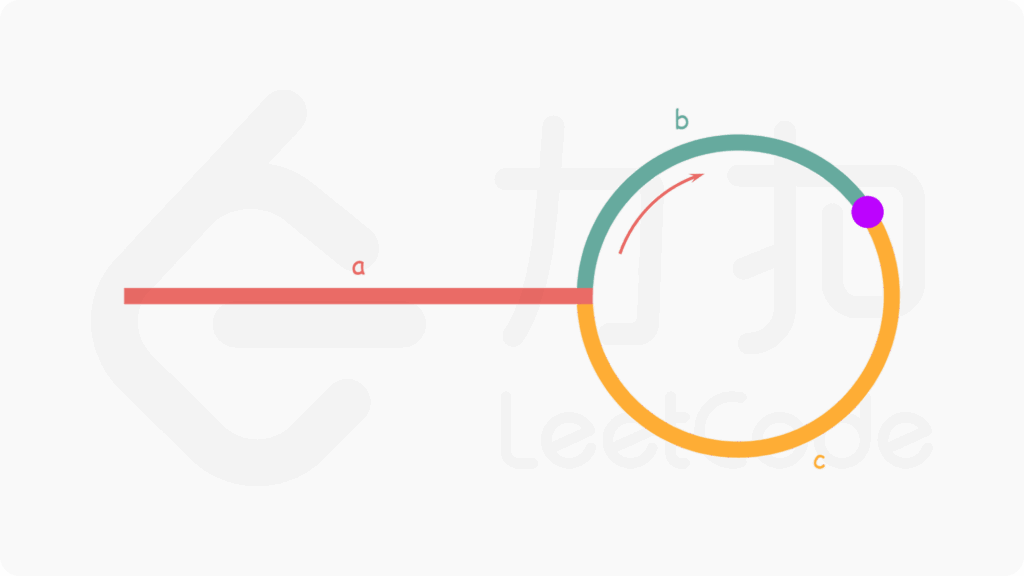
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(slow == fast){
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != slow){
cur = cur.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return cur;
}
}
return null;
}
}
合并两个有序链表
用一个新的节点引出来就比较简单了。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode pre = dummy;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
pre.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
pre.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
if(list1 == null){
pre.next = list2;
}else{
pre.next = list1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
两数相加
模拟题
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode cur1 = l1;
ListNode cur2 = l2;
ListNode cur3 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = cur3;
int preV = 0;
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null){
int sum = cur1.val + cur2.val + preV;
preV = 0;
if(sum >= 10){
preV = 1;
sum = sum - 10;
}
ListNode node =new ListNode(sum);
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
while(cur1 != null){
int sum = cur1.val + preV;
preV = 0;
if(sum == 10){
preV = 1;
sum = sum - 10;
}
ListNode node =new ListNode(sum);
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != null){
int sum = cur2.val + preV;
preV = 0;
if(sum == 10){
preV = 1;
sum = sum - 10;
}
ListNode node =new ListNode(sum);
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if(preV == 1){
ListNode node =new ListNode(1);
cur.next = node;
}
return cur3.next;
}
}
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
最直观的方式,就是遍历出长度,然后找到倒数第N个节点的前驱,后继。然后更改即可。
如果要一边扫描的话,就要用双指针,右指针先走,当右指针到边界的时候,左指针的下一个就是要删除的点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode l = dummy;
ListNode r = dummy;
// 右指针先前进 n 次
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
r = r.next;
}
while (r.next != null) {
r = r.next;
l = l.next;
}
l.next = l.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
两两交换链表中的节点
要用三指针。得画图理解, 光看代码有点抽象。
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return head;
if(head.next == null) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode temp = dummy;
ListNode cur1 = head;
temp.next = cur1;
ListNode cur2 = head.next;
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null){
cur1.next = cur2.next;
cur2.next = cur1;
temp.next = cur2;
temp = cur1;
cur1 = temp.next;
if(cur1 != null) cur2 = cur1.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
K个一组反转链表
像模拟题,主要是裁出来要反转的部分+细节处理。有点难。
贴一个题解。
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy; // 上一段的最后一个节点
ListNode end = dummy; // 本段最后一个节点 刚好最后一个节点
while (end.next != null) {
for(int i = 0 ; i < k && end != null; i++){
end = end.next;
}
if(end == null){// 如果直接到头了,那就说明没有满足 k 个
break;
}
ListNode start = pre.next;// 此处是为记录原始未反转段的起始节点
ListNode nextStart = end.next;// 记录下一个阶段 起始点
end.next = null;// 此处是为了进行后面的反转操作,断开此处链接,让后面反转操作知道截断点在哪里
pre.next = reverse(start); // 反转操作
start.next = nextStart;// 反转之后,start节点实际是已经最后一个节点了,为了和后面的划分段链接,让他的下一个节点连接上下一段的起始点即可
pre = start; // pre再次来到下一段的上一个节点,也就是本段的结尾点
end = pre; // 结束点,准备开始下一段的循环找 k 长度的段操作
}
return dummy.next; // 返回最开始的哨兵
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head){
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null){ // 交换操作
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre; // 返回哨兵,此处是新的翻转序列的起始节点
}
随机链表的复制
用hashMap存旧节点和新节点的映射,两次遍历
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
// 构造hashmap映射 旧-新
if(head == null) return null;
Map<Node, Node> mp = new HashMap<>();
Node dummy = new Node(-1);
Node cur = head;
Node newcur = dummy;
while(cur != null){
Node n = new Node(cur.val);
mp.put(cur, n);
newcur.next = n;
newcur = n;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 接下来维护random
newcur = dummy.next;
cur = head;
while(newcur != null){
// 要维护newcur的random 只需要找到cur.random映射的新节点
newcur.random = mp.get(cur.random);
newcur = newcur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
排序链表
如果要实现O1空间复杂度,很麻烦,需要使用迭代的方式自底向上归并排序,此处只记录归并排序的递归版本(自顶向下)。
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 递归终止条件:空链表或单节点链表
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 找到链表中点
ListNode mid = findMiddle(head);
// 分割链表
ListNode rightHead = mid.next;
mid.next = null; // 切断链表
// 递归排序左右两部分
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(rightHead);
// 合并两个有序链表
return merge(left, right);
}
// 使用快慢指针找到链表中点
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 合并两个有序链表
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
curr.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
curr.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
// 连接剩余部分
curr.next = (l1 != null) ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
合并K个升序链表
用优先队列来做是最直观的,优先队列能自动组织队列的元素,复杂度为logn级别。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
// 用优先队列来存节点 优先队列的排序复杂度是logn的
class priorityNode implements Comparable<priorityNode>{
int val;
ListNode ptr;
public priorityNode(int _val, ListNode _ptr){
this.val = _val;
this.ptr = _ptr;
}
public int compareTo(priorityNode n){
return this.val - n.val;
}
}
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
PriorityQueue<priorityNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(ListNode n:lists){
if(n != null) pq.offer(new priorityNode(n.val, n));
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
// 优先队列取出来的 一定是最小的
priorityNode p = pq.poll();
cur.next = p.ptr;
cur = cur.next;
if(p.ptr.next != null){
// 把取出来的点的next 加入队列
pq.offer(new priorityNode(p.ptr.next.val, p.ptr.next));
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}